Validation Method for Non-rigid Registration
We have presented a novel validation method for non-rigid image registration
in [6,7].
It is based on applying the
registration to misaligned images, generated from plausible deformations
simulated by biomechanical models using finite element methods.
For this, pre- and post-contrast image sets,
which showed no motion, were selected from a large patient data
base (Figure 1a,b).
Then a finite element model of the breast was generated by segmenting
the breast into fatty and glandular tissue and enhancing lesion via
ANALYZE,
extracting the breast surface via
vtk and meshing the breast
into 10-noded tetrahedral elements via the
ANSYS FEM package.
Material properties from literature were then
assigned to the element in accordance to the image segmentation,
surface displacements applied and a solution obtained with the ANSYS
FEM package. Figure 1(d,e) show an animation of the simulated
deformation for a regional displacement of 10mm on the breast
surface.
Images of these deformed breasts were then generated by quadratic
shape interpolation of the 10-noded tetrahedral elements (Figure 1f).
Finally, the pre-contrast images were registered to the FEM deformed
post-contrast images (Figure 1h) and the registration accuracy was
determined at each voxel position within the breast.
Note that the same method can be applied to other organs as
long as a plausible finite element model can be generated.
(a)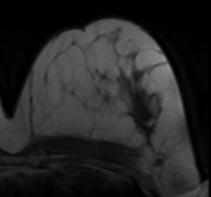 (b)
(b)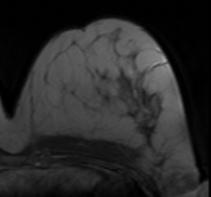 (c)
(c)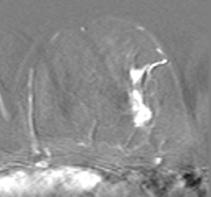
(d)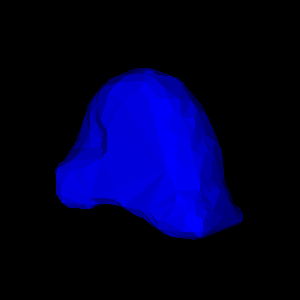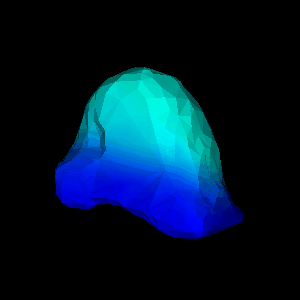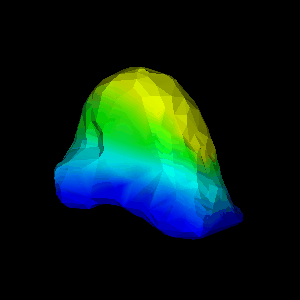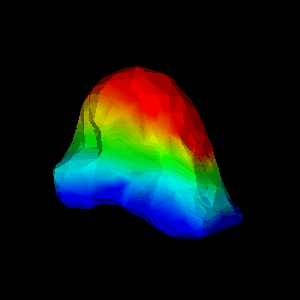
 (e)
(e)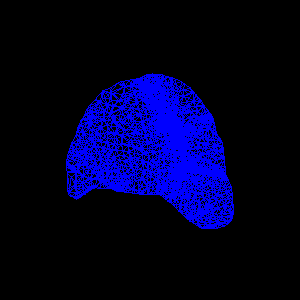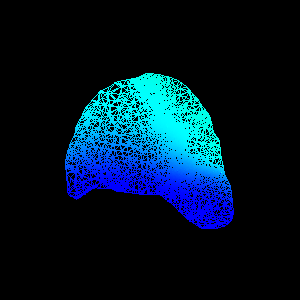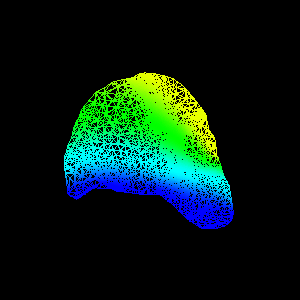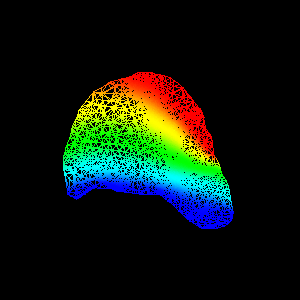
(f) (g)
(g)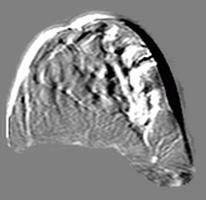 (h)
(h)
Figure 4: Illustration of validation strategy:
2D example slice of (a) original pre-contrast
image, (b) original post-contrast image (c) difference image (b-a);
(d,e) simulated deformation (regional displacement) showing
in colour magnitude of displacement at
(d) surface and (e) cut through finite element model;
(f) deformed post-contrast image within model (g)
difference image after deformation (f-a),
(h) difference image after non-rigid
registration of (a) to (f)
References:
[7] J. A. Schnabel, C. Tanner, A. D. Castellano-Smith, A. Degenhard,
M. O. Leach, D. R. Hose, D. L. G. Hill, D. J. Hawkes.
Validation of
non-rigid image registration using finite element methods:
Application to breast MR images. IEEE Transactions on Medical
Imaging, vol. 22(1), 2003. In press.
[6] J. A. Schnabel, C. Tanner, A. Castellano-Smith, M. O. Leach,
C. Hayes, A. Degenhard, R Hose, D. L. G. Hill,
D. J. Hawkes. Validation of non-rigid registration using finite
element methods. In Proc. Information Processing in Medical Imaging
(IPMI'01), University of California at Davis, 2001, 18-22 June 2001,
vol. 2082 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 344-357, Springer
Verlag, 2001.
Last modified: Sun Feb 9 12:50:44 GMT 2003
 (b)
(b) (c)
(c)

 (e)
(e)
 (g)
(g) (h)
(h)